ITSM
A Catalyst for Innovation and Development.
Nilavanam Technologies’ Information Technology Service Management (ITSM/Helpdesk) is a Unified approach to designing, delivering, managing, and improving IT & NON-IT services within an organization. It focuses on aligning IT services with the business’s needs, ensuring that technology effectively supports organizational goals. By implementing ITSM practices, companies can enhance service quality, improve customer satisfaction, and optimize costs, making it a crucial aspect of modern IT operations.
The core components of ITSM include Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement (CSI). Service Strategy involves defining the overall direction for service management and aligning IT services with business objectives. Service Design focuses on creating efficient and reliable services that meet user needs, while Service Transition manages the process of moving new or changed services into production with minimal disruption. Service Operation oversees the day-to-day management of IT services, ensuring they are delivered effectively and efficiently. Ultimately, CSI strives to continually enhance service quality through ongoing analysis and improvement initiatives.
The benefits of ITSM are substantial, including increased operational efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, cost reduction, and improved risk management. By streamlining processes and enhancing service delivery, organizations can respond more effectively to the evolving needs of their businesses. Popular frameworks, such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology), and ISO/IEC 20000, provide best practices and standards that guide organizations in implementing effective IT Service Management (ITSM) strategies.
ITSM Components
IT & NON-IT Service Management (ITSM) comprises several key components that work together to ensure the effective management and delivery of services. Below are the primary components of ITSM:
Service Strategy
Purpose: Defines the overall strategy for service management.
Key Activities:
- Identifying customer needs and market trends.
- Aligning IT services with business objectives.
- Developing service portfolios and financial management strategies.
Service Design
Purpose: Focuses on designing new services and modifying existing ones.
Key Activities:
- Creating service catalogs that outline available services.
- Planning for capacity, availability, and continuity.
- Designing processes and systems to support service delivery.
Service Transition
Purpose: Manages the transition of new or changed services into the live environment.
Key Activities:
- Implementing change management to control service changes.
- Conducting release management to deploy new services.
- Ensuring proper knowledge transfer and training for staff.
Service Operation
Purpose: Oversees the day-to-day delivery and management of IT services.
Key Activities:
- Managing incidents to restore normal service operation quickly.
- Handling problems to identify and eliminate root causes.
- Fulfilling service requests from users efficiently.
Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Purpose: Aims to continually improve the quality of IT services.
Key Activities:
- Analyzing performance metrics and feedback.
- Identifying areas for improvement and implementing changes.
- Utilizing the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model for ongoing enhancements.
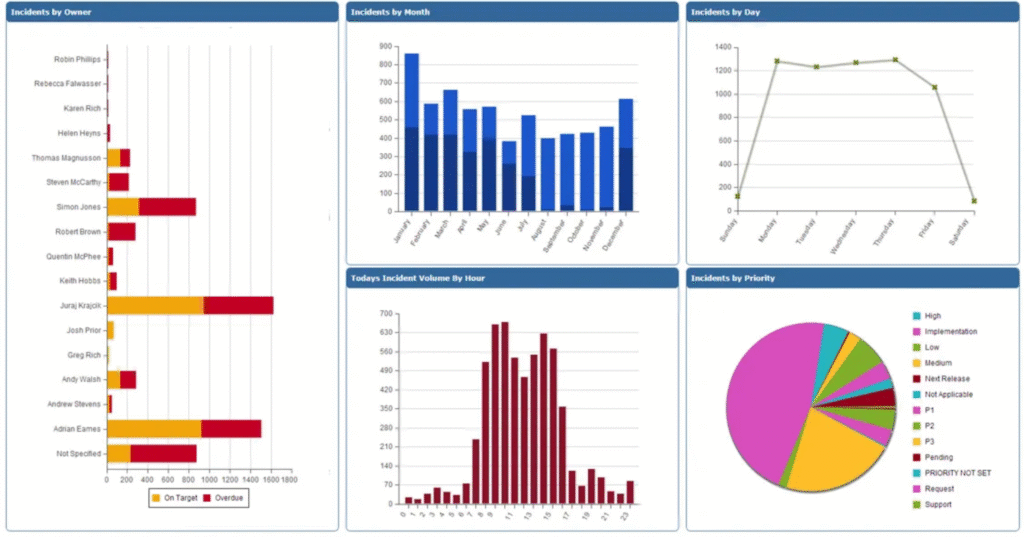
ITSM Ticketing
ITSM Ticketing is a fundamental aspect of IT Service Management that involves the process of logging, tracking, and managing requests and incidents reported by users. The ticketing system serves as the backbone for service delivery, enabling IT teams to efficiently handle issues, fulfill requests, and ensure effective communication between users and support staff.
Ticket Creation
- Users can create tickets via multiple channels, such as email, web forms, or direct calls to the help desk.
- Each ticket includes crucial details like the user’s information, issue description, priority level, and any relevant attachments.
Ticket Categorization and Prioritization
- Tickets are categorized based on the type of issue (e.g., incident, service request) and prioritized according to urgency and impact on business operations.
- This helps in routing tickets to the appropriate support teams and ensures critical issues are addressed promptly.
Tracking and Management
- Ticketing systems allow for real-time tracking of ticket status, providing visibility into the progress of each request.
- IT teams can update ticket statuses, add notes, and communicate with users directly through the ticketing platform.
Automation and Workflow Management
- Many ticketing systems offer automation features, such as auto-assignment of tickets to specific teams or escalation procedures for high-priority issues.
- Workflow management ensures that tickets follow a predefined process from creation to resolution, improving efficiency.
Reporting and Analytics
- Ticketing systems provide reporting tools that help analyze ticket data, identify trends, and measure performance metrics like response times and resolution rates.
- This data is valuable for continual service improvement and helps in identifying areas that require additional resources or training.